Have you heard of floatation therapy?
Blants NZ supplies several float centres across New Zealand with their Natural Epsom Salt, so we thought we should give this wonderful wellbeing solution a mention.
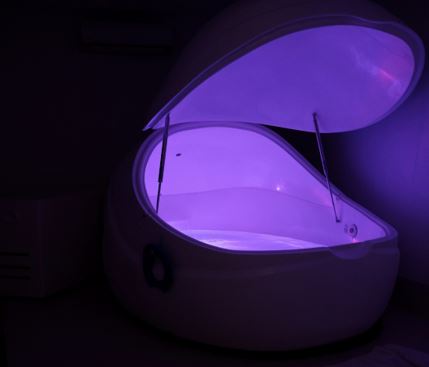
It’s one of the easiest, most relaxing and beneficial things you can do for your mental and physical well-being. It involves lying in a specially designed pod that is filled with 30cm deep body-temperature water, usually for about an hour. The water is super-saturated with Epsom Salt (Magnesium Sulphate), which makes the water more buoyant than the Dead Sea, ensuring that you float effortlessly.
Floating is also known as REST – Restricted Environmental Stimulation Therapy. The Float Pod is designed to restrict light and sound, meaning your body and mind can switch off completely from day-to-day life stresses. It is the optimum environment for you to relax and revitalise. You can often choose to have a light on or listen to relaxing music if you prefer that to total silence.
Almost everyone can float (although it may not appeal to all people, and there are a few restrictions eg if you have a serious heart condition or uncontrolled epilepsy, and some centres have age restrictions). Floating is enjoyed by people who are experiencing anxiety or stress; people who play sports or do physical training and want to speed up recovery and achieve optimum results; people with pain; people who need to learn or be creative, and people who simply want an hour to switch off from the hustle and bustle of life and experience the ultimate in peace, quiet and relaxed mindfulness.
Floatation causes a major reduction of muscular tension throughout your whole body, which can last for days after your float session. Floating also affects the nervous system by:
These will be experienced as a lowering of your body’s response to stress.
This relaxation response is achieved in the float pod with no effort or training required, making it easy and accessible to all users. Even people who have felt anxious about floating find that they are able to relax.
How does floating achieve this?
As with many things in life, there is no one concise answer. But theories include:
1- Deep Relaxation
Floating gives you a deep relaxation of all your muscles, that can be achieved with no effort, unlike other techniques such as meditation or biofeedback that involve time, patience, training and discipline.
2- Anti-gravity theory
Our upright posture exerts huge gravitational pressure on our feet and spine. We compensate for gravity by adopting rigid postures and then develop chronic muscular tension in certain areas. This tension can lead to other issues like shallow breathing and high blood pressure.
And it’s not just our body that’s affected – our brain is constantly computing how to keep our body upright and fighting gravity. Our central nervous system is basically pre-occupied with dealing with gravity.

Floating effortlessly in the pod reduces gravitational muscular tension, reducing the bulk of stimuli arriving at the nervous system. The brain and autonomic nervous system are basically given a true rest.
3- Brain wave theory
Research involving measurement of the brain by EEG (e.g. – Thomas Budzynski, Biofeedback Institute of Denver) shows that floating increases the production of theta brain waves. We normally experience this state briefly as we fall asleep and wake up. Floaters experience this state, yet remain awake, enabling vivid imagery and the use of positive visualisation.
4- Left and right brain theory
The left-brain hemisphere (associated with analytical and logical thought) is normally dominant. The right brain is more nonverbal, intuitive and nonlinear. When floating ‘turns off’ external stimuli, the dominant left side of the brain has little to do and the right side is given a chance to shine. It’s this that increases productivity, performance and efficiency, as well as feelings of increased competence and confidence, which can make a great deal of difference to someone struggling with feeling anxious or low about themselves.
5 – Biochemistry
Processes within the brain trigger hormones and neurotransmitters that affect the body. Floating has an effect on these brain chemicals.
John Turner (neuroendocrinologist) and Thomas Fine (psychologist) of the Medical College of Ohio have shown that floatation lowers the levels of norepinephrine, adrenaline, cortisol and ACTH. These chemicals are directly linked to stress and stress-related illnesses, such as poor sleep, feeling anxious or depressed.

Floating also causes increased secretion of endorphins that relieve pain and provide a feeling of euphoria.
6 – Biofeedback
When floating with no external stimuli, there can be intense awareness of internal signals, combined with the very deep state of relaxation. Research has shown that the most important prerequisite for gaining control over the body through biofeedback is relaxation. Relaxation is achieved effortlessly in the float pod, reducing the time you have to spend learning a deep relaxation technique like meditation or yoga.
7 – Sensory isolation
In effect, the brain becomes bored because there is no work for it to do in the float pod – no light, sound or skin response to process. The brain wants something to do so it will focus on whatever it is given. Now imagine playing a recording of restful, relaxing music or positive statements to that information-hungry brain …
8 – Epsom salt benefits
Magnesium (Epsom salt is magnesium sulphate) has many benefits for the body and these are best accessed when it is absorbed through the skin. Some of the benefits of magnesium, that are pertinent to improving your mental and physical well-being are:
Now you can’t truly replicate floating in your bath at home, but there are certainly elements you can add to your wellbeing routine.